Case study: How the blockchain automatises will processing
---
Automation, thanks to blockchain and technologies, streamlines the will drafting process
1. Case of fact
You are an attorney writing a will for your client. The will is simple and a tad ridiculous in this example. It stipulates that upon the parent’s death, their two kids must be separately married in order for them to split the estate. If one kid is married and the other kid is not, the kid that is married gets the entire estate. For simplicity the assets are all liquid in this example.
2. Blockchain application
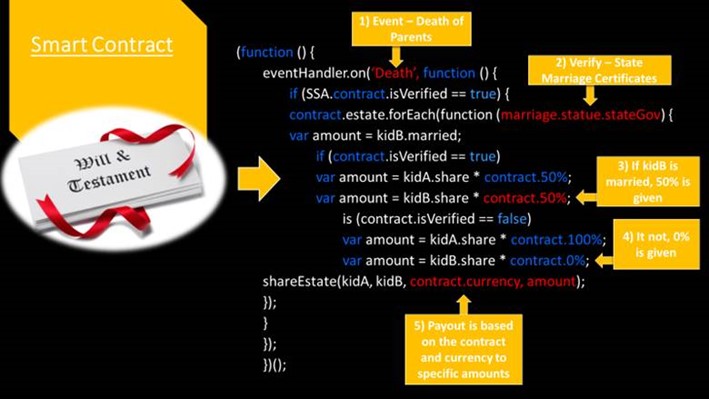
The will is written in Word. Then it is then codified looking for those parameters that are contingencies or possibly subject to change. Saved in a smart contract on a blokchain, likely Ethereum. It is now in an immutable state but has actionable items imbedded in it. The only people that have access to this document are the attorney that drew it up and her client. Once it is on the blokchain, the smart contract – with the coded parameters - starts checking every day through a trusted source, called an oracle (affirmed public record), to see if both parents are alive. One day the computer identifies that the parents have passed.
Heartless, the computer jumps to the next task to determine if both kids are married. Through another API computer call to that oracle, it finds out that one kid is married and the other kid is not, and subsequently sends 100% of the liquid assets to the kid that is married. This is a self-executing smart contract on a blokchain being baked out now.
Blockchain Enabled Digital Will – Trusts & Estates
3. Challenges
The biggest challenge now is education. Helping people understand how all of this works. Second is standards. Right now there isn’t uniform standards that the legal industry has embraced, so people are working on this now. Lastly is the technology. While this can be done, it is still a bit onerous to code out. In the coming years applications that see the words, convert them to actionable code will flourish making this far easier to use across all contracts.
4. Conclusion
Clearly the benefits here are that you can take a manual process and automate it, hopefully for ease and less errors. Once the contract (Trust) has been written, it is self-executing. While certainly some issues will arise, the thrust is that this will create efficiency in the industry, and should provide fodder for litigation too.
Related links
Main menu






